In the realm of laboratory science and research, precision and efficiency are paramount. Among the numerous tools and equipment used in labs, Eppendorf Tubes, commonly referred to as EP Tubes, play a crucial role in various scientific processes. These tubes are essential for storing, handling, and transporting small volumes of liquids, particularly in molecular biology, biochemistry, and related fields. This article delves into the definition, applications, and methods of filling EP Tubes, with a special focus on the use of automated filling and capping machines, such as the SFXB XBTEP-30 Desktop Ceramic Pump Filling and Capping Machine.
What is an EP Tube?
An EP Tube, or Eppendorf Tube, is a type of centrifuge tube used in laboratories for centrifuging small volumes of liquids, typically between 0.5 mL and 2.0 mL. These tubes are designed to withstand high centrifugal forces and are made from high-quality polypropylene or other durable materials that ensure they can handle the rigorous demands of laboratory procedures. EP Tubes are named after the Eppendorf company, a well-known manufacturer of laboratory equipment, and have become a standard tool in many scientific workflows.
EP Tubes are characterized by their conical shape, which allows for efficient centrifugation and easy removal of supernatants. They are also designed with a secure, snap-on cap to prevent leakage during handling and centrifugation. These tubes are autoclavable, making them suitable for sterile laboratory applications.

Applications of EP Tubes
EP Tubes are versatile and are used in a wide range of laboratory applications, including:
1. Centrifugation: EP Tubes are designed for centrifuging small volumes of liquids. They are commonly used in protocols such as DNA extraction, protein precipitation, and cell pelleting.
2. Sample Storage: The tubes are ideal for storing small volumes of biological samples, such as DNA, RNA, proteins, and other reagents, at low temperatures.
3. Mixing and Reaction: EP Tubes can be used as mini reaction vessels for mixing small volumes of liquids. Their conical shape facilitates efficient mixing by vortexing.
4. Freezing: EP Tubes are designed to withstand extremely low temperatures, making them suitable for long-term storage of samples in freezers.
How to Fill EP Tubes
Filling EP Tubes accurately and efficiently is critical to ensuring the integrity of laboratory samples and the success of downstream applications. Depending on the volume and the nature of the liquid being filled, different methods can be employed.
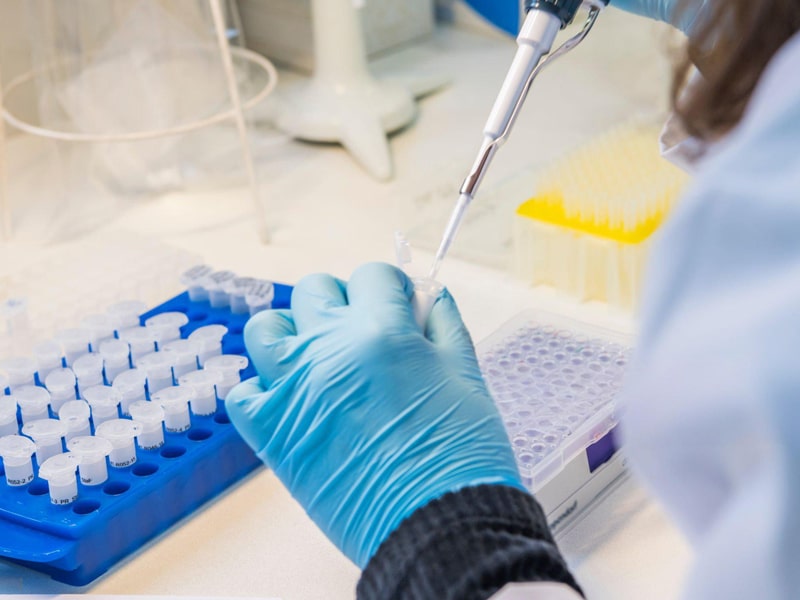
Manual Filling
Manual filling of EP Tubes is a common practice in laboratories, particularly when dealing with small volumes. Here’s a step-by-step guide for manually filling EP Tubes:
1. Prepare the Sample: Ensure that the sample is properly prepared and ready for transfer into the EP Tube. If the sample is viscous or sensitive to temperature, take necessary precautions to maintain its integrity.
2. Use a Pipette: Use a micropipette or a pipettor to accurately measure and transfer the sample into the EP Tube. Pipettes are available in various volumes, so choose one that matches the volume of the sample being transferred.
3. Avoid Aeration: When transferring liquid into the EP Tube, avoid creating air bubbles, as they can interfere with downstream applications such as PCR or spectrophotometry.
4. Label the Tube: Properly label the EP Tube with the sample name, date, and any other relevant information. Use a permanent marker and ensure the label is legible.
5. Secure the Cap: Once the sample is inside, snap the cap securely to prevent leakage.

Automated Filling
While manual filling is straightforward, it can be time-consuming and prone to human error, especially when dealing with large numbers of samples. Automated filling machines, such as the SFXB XBTEP-30 Desktop Ceramic Pump Filling and Capping Machine, offer a high-efficiency solution for filling EP Tubes.
The XBTEP-30 is a desktop ceramic pump filling and capping machine designed for small to medium-sized laboratories. This machine is capable of filling and capping EP Tubes with high precision and speed, making it an ideal choice for labs that need to process multiple samples quickly and accurately.
Key features of the XBTEP-30 include:
– High Precision: The machine is equipped with a ceramic pump that ensures accurate filling, even for small volumes.
– Speed: The XBTEP-30 can fill and cap multiple EP Tubes in a short amount of time, significantly increasing laboratory throughput.
– Ease of Use: The machine is user-friendly and comes with an intuitive interface that allows for easy operation.
– Compatibility: The XBTEP-30 is compatible with a wide range of EP Tubes and can be easily integrated into existing laboratory workflows.
Using the XBTEP-30 for filling EP Tubes involves the following steps:
1. Prepare the Machine: Turn on the machine and allow it to warm up if necessary. Ensure that all components are clean and free from any residual substances.
2. Load the EP Tubes: Place the EP Tubes into the machine’s feeding system. The machine is designed to handle multiple tubes at once, allowing for efficient batch processing.
3. Set the Parameters: Use the control panel to set the filling volume, filling speed, and other parameters as needed. The machine’s ceramic pump allows for precise control over the filling process.
4. Start the Filling Process: Initiate the filling process. The machine will automatically fill each EP Tube to the specified volume and then cap it securely.
5. Monitor the Process: Keep an eye on the machine during the filling process to ensure that everything is running smoothly. If any issues arise, stop the machine and troubleshoot.
6. Unload the Tubes: Once the filling and capping process is complete, remove the EP Tubes from the machine and store them appropriately.
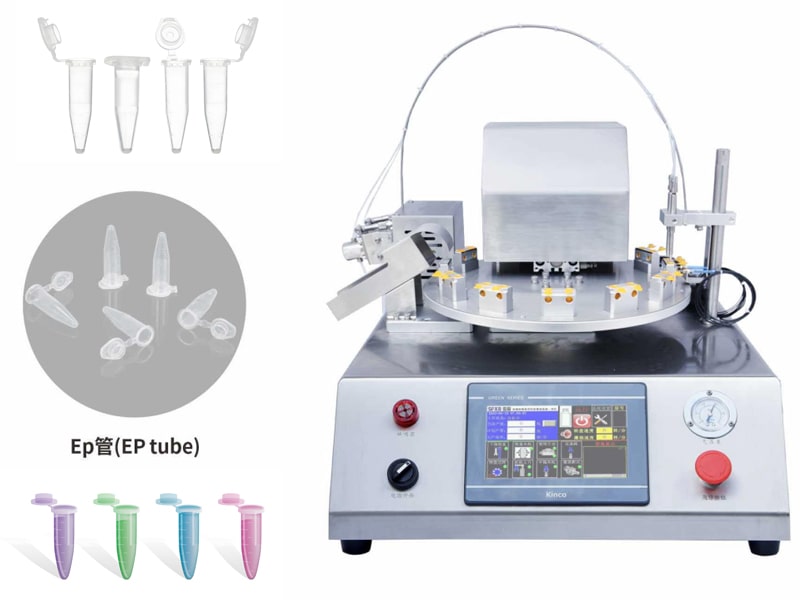 |
XBTEP-30 Desktop EP tube automatic filling and capping machine
Suitable for EP tube filling gland, easy to use |
Benefits of Using Automated Filling Machines
Automated filling machines like the XueBaPack XBTEP-30 offer several advantages over manual filling, including:
– Increased Efficiency: Automated machines can fill and cap multiple EP Tubes much faster than manual methods, freeing up valuable time for laboratory staff.
– Improved Accuracy: The use of a ceramic pump ensures that the filling process is precise, reducing the risk of errors and variability.
– Reduced Labor Costs: By automating the filling process, laboratories can reduce their labor costs and allocate resources to other critical tasks.
– Enhanced Consistency: Automated machines ensure that each EP Tube is filled to the same volume, maintaining consistency across samples.
Best Practices for Handling EP Tubes
To ensure the longevity and performance of EP Tubes, as well as the integrity of the samples they contain, it’s important to follow best practices for handling and storage:
1. Avoid Overfilling: Overfilling EP Tubes can lead to leakage during centrifugation or storage. Always fill the tubes to the recommended volume.
2. Label Clearly: Proper labeling is essential for keeping track of samples. Use a permanent marker and include all relevant information, such as the sample name, date, and concentration.
3. Store Appropriately: EP Tubes should be stored in a cool, dry place when not in use. For samples that require refrigeration or freezing, ensure that the tubes are stored at the appropriate temperature.
4. Avoid Exposure to Extremes: While EP Tubes are designed to withstand extreme conditions, prolonged exposure to high temperatures or harsh chemicals can compromise their integrity. Handle the tubes with care and avoid unnecessary exposure to such conditions.
5. Clean and Decontaminate: After use, properly clean and decontaminate EP Tubes to prevent cross-contamination. Autoclaving is a recommended method for sterilizing used tubes.
Conclusion
EP Tubes are indispensable tools in laboratory settings, providing a reliable and efficient way to handle small volumes of liquids. Whether filled manually or using automated machines like the SFXB XBTEP-30, EP Tubes play a critical role in ensuring the success of various scientific applications. By understanding how to properly fill and handle EP Tubes, laboratory professionals can optimize their workflows, reduce errors, and achieve better results in their research and experiments.
| References: | |
| 1. | ASTM International. (2022). ASTM E438-92(2022): Standard Specification for Glasses in Laboratory Apparatus. Link |
| 2. | WHO. (2020). Laboratory biosafety manual (4th ed.). Link |
| 3. | FDA. (2023). 21 CFR Part 211 – Current Good Manufacturing Practice for Finished Pharmaceuticals. |






Comments